
Applications for The Victory Academy Sixth Form are now open! To apply please click here.

Applications for The Victory Academy Sixth Form are now open! To apply please click here.
“Design is a funny word. Some people think design means how it looks. But of course, if you look deeper, it’s really how it works.” Steve Jobs
Why does our curriculum look like this?
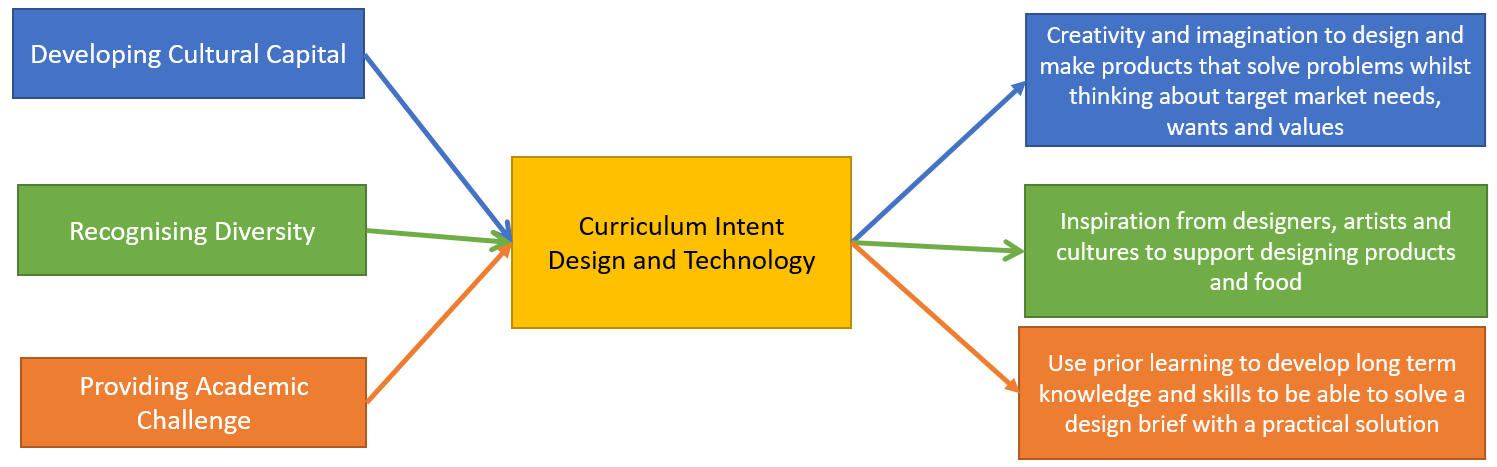
Design and Technology is an inspiring, rigorous and practical subject. Design and Technology encourages students to learn to think creatively to solve problem. At The Victory Academy, Design and Technology inspires creativity and imagination, empowering students from Key Stage 3 to Key Stage 5 to design and create innovative products, including food, that solve real-world problems. By considering the needs, wants, and values of target markets, drawing inspiration from renowned designers, artists, and global cultures, and building on prior learning, students develop the skills and knowledge needed to respond to design briefs with practical, impactful solutions. This journey fosters critical thinking, collaboration, and a deep appreciation for design's ability to shape the world around us. We aim to, wherever possible, link work to other disciplines such as mathematics, science, engineering, computing and art. Ultimately, we aim for students to be aspirational and ready for the next step in their life journey.
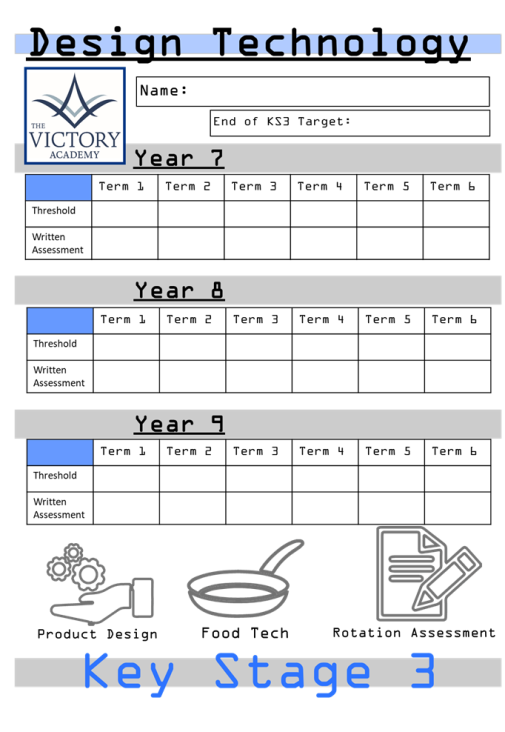
Design and Technology will be taught to a high standard, with each subject area given equal weighting over all key stages. There will be evidence in each of these areas in the Design and Technology folders, which will also show clear progression across the key stages as they pass up through each year group.

For Key Stage 3, Design and Technology is taught across Product Design and Food and Nutrition, with each discipline worked over a two-term rotation. This is to allow the students to experience a wide range of fun and exciting projects that teach them valuable skills in the workshop, computer skills and kitchen. This allows students to understand different materials and ingredients and how they work.
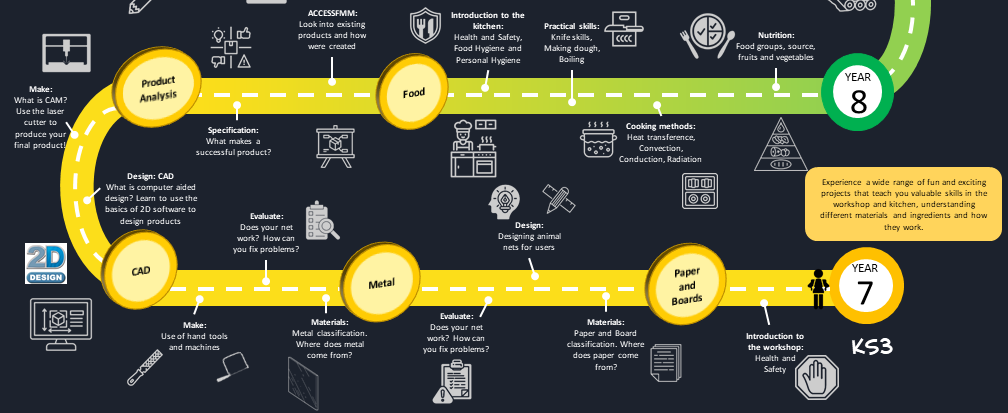
Paper and Boards - In Year 7 students join us with various skills and knowledge. For this rotation, all students will be understanding the sources, properties, names and uses and fundamental practical skills of creating models.
Metal - After Paper and Boards rotation, all students will be using the model they created to generate a metal product. The students will learn and develop knowledge of sources of metal, properties, names and uses. Also the practical skills through health and safety and tool work
CAD/CAM - As part of the rotations, students will be learning about CAD and CAM theory, application and processes. The students will use their knowledge to create a practical outcome.
Product Analysis - After the CAD/ CAM rotation, students will learn how to study existing products through ACCESSFMM which will developing their understanding of iterative design process.
Food Technology - In year 7 students join us with varying skills and knowledge. They will understand and use health and safety and hygiene rules in a kitchen environment. Students will master basic knife skills, cooker skills, and understanding recipes as well as theory knowledge.
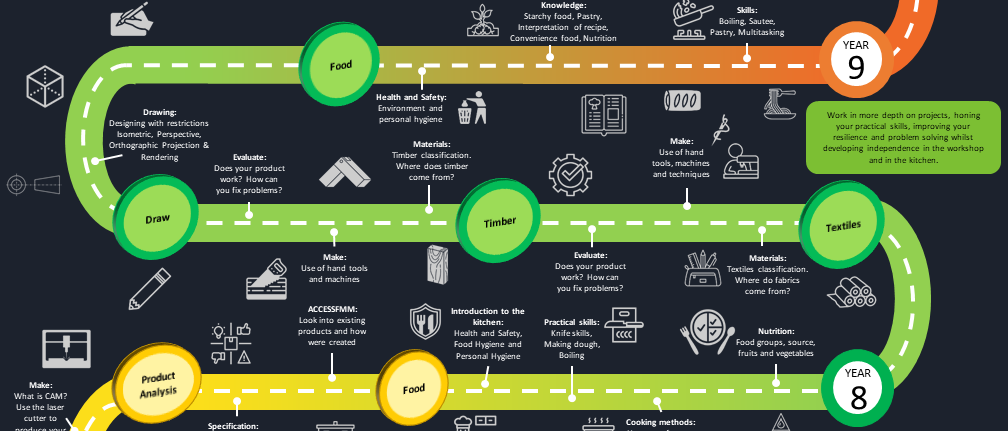
Textiles - In Year 8 students will understand the foundation knowledge of textiles, the sources, properties, names, uses and sustainability of all materials and the effect on the environment. Students will be designing, developing ideas through the iterative design process, before producing a final design idea. This design idea will then be created using the correct materials, tools and equipment and finishing process, whilst the students will comprehend the safety rules, machine knowledge and steps in order to produce their product.
Timber - In Year 8 students will understand the foundation knowledge of timber, the sources, properties, names, uses and joining of materials. The student will be creating a product by using the correct materials, tools and equipment and finishing process, whilst the students will comprehend the safety rules, machine and tool knowledge and steps in order to produce their product.
Food Technology - The students will become more confident will knife skills and other methods of cooking including rubbing in methods, and multi-tasking practical. Students will further their knowledge of nutrition, expanding on the concepts from last year, and gain an understanding of a balanced diet. They will apply their knowledge of nutrition to some case studies to demonstrate how knowledge and research may be used. Students learn how to understand a recipe and are encouraged to modify recipes to suit their personal and families’ needs; such as special dietary needs (health and allergen), religious and cultural beliefs and personal likes and dislikes.
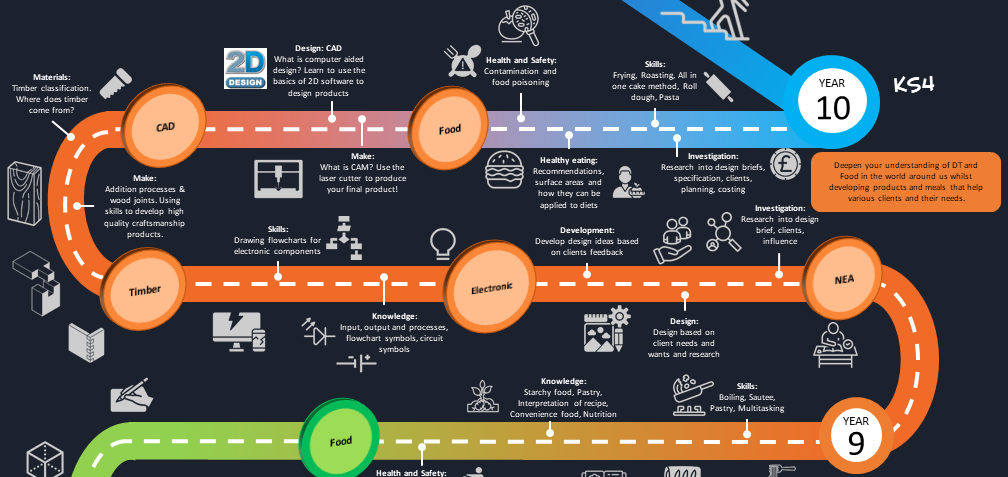
Coursework - In Year 9 we start to engage the students in coursework skills to thoroughly understand what the expectations at GCSE. The students go through research, client analysis and designing a product with effective annotations and developments to further enhance their ideas.
Timber - Students then use skills previously taught and develop practical skills to make the base on the product the students have designed. This expands the students understand of different joining methods and finishes that can be applied to timber.
CAD/CAM and Polymer - Students generate a foundation knowledge of sources, properties, names and uses of Polymers. Students will also recap skills on how to use CAD and CAM to generate parts of the product and produce a 3D model of their design idea from their coursework rotation.
Electronics - Students to recap on Electronic theory taught in Science in Year 8 and visibly see how the subject links with Design and Technology. Students will engage in learning circuits, flow charts and how to successfully wire their product. Students also go through an effective evaluation when the product has been completed which include testing and improvements similar to when Year 11 students complete their coursework.
Food Technology - In this year, students become more confident with knife skills and the use of the cooker. Students will further their knowledge of nutrition and balanced diet, expanding on the concepts from previously taught. The main concept is healthy eating focusing on how to make popular food choices healthy. Students will also understand how to modify a recipe.
At the end of every term in the two-term rotation, the students will be completing a written assessment based on their theory knowledge learnt throughout the term which is marked out of 50. Students can then develop upon their gaps before the larger end of rotation test which teachers have marked thoroughly. The questions in the assessments are modified from the GCSE past papers which boost confidences in our students from Year 7 up to Year 9.
This data is the inputted into their folder sheets which allows the student to see their; End of Key Stage 3 Target, Threshold (their current practical or coursework grade) and their Written Assessment grade. This folder sheet stays with the student from when they first arrive in Year 7 up until the end of Key Stage 3.
Also in the student’s folder, there is a Health and Safety record sheet which includes the health and safety policy of Kitchen, IT and Workshop rules and by signing and dating below, the student accepts responsibility of the consequences of breaking these rules which may result in a reconciliation, being reset from the teaching room and/ or removed from the course. The teacher may also complete a hand tool or machine report as to show that the students have been shown how to safely use the equipment.

In Design and Technology, we run an after-school club, where the students can develop their practical skills in Textiles, Woodwork and Cooking that may help them with lifelong skills. For example, sewing on a button or repairing clothing, being able to cut and shape wood into objects and cooking well-loved foods and treats.
Choosing GCSE Eduqas Design and Technology or GCSE Eduqas Food Preparation and Nutrition opens doors to creativity, innovation, and essential life skills. In Design and Technology, students explore product design through technical knowledge and hands-on practical work, inspired by real-world contexts and problem-solving challenges. In Food Preparation and Nutrition, students develop a deep understanding of food science, nutrition, and culinary skills, rooted in practical applications and real-life scenarios. Both subjects equip learners with the technical expertise, creativity, and confidence needed to thrive in further education, careers, and everyday life.
Studying Food Preparation and Nutrition will equip students with the knowledge, understanding and skills required to cook and apply the principles of food science, nutrition and healthy eating. It will encourage students too cook and be able to make informed decisions about food and nutrition and will also allow students to acquire knowledge and understanding required in order to be able to feed themselves and others affordably and nutritiously, now and later in life.
This qualification in food and preparation will enable students to make connections between theory and practice so that they are able to apply their understanding of food science and nutrition to practical cooking. The content relates to the study of both food and drinks.
Students will develop skills in:
Assessments - In Year 10, the students will be assessed at the end of each term on written assessment that prepare the students for the GCSE exam which they will sit in Year 11. They will also be assessed on practical skills learnt and developed each term.
In Year 11, the students will have two components to complete. Component 1 is the written exam based on the principles of food preparation and nutrition which is a 1 hour and 45-minute exam, marked out of 100 and is 50% of the qualification. Component 2 is made up of two tasks. Task 1 being a food investigation assessment which will take the students 8 hours and is 15% of the qualification. It will involve practical experimental work and written work based on a specific food commodity such as bread or pastry. Task 2 being a food preparation assessment which will take the students 12 hours to complete and is 35% of the qualification. It will involve; research to respond to a given brief plus planning, preparation, cooking (3 hour session) and presentation of the three dishes plus accompaniments (if appropriate) to form a menu.
Through studying Design and Technology, students will be prepared to participate confidently and successfully in an increasingly technological world; and be aware of, and learn from, wider influences on design and technology, including historical, social/cultural, environmental and economic factors.
The course will offer students the opportunity to solve real problems by designing and making products.
Students will study, technical principles and designing and making principles which will allow them to develop knowledge and understanding of design and technology, its impact on daily life, and develop a broad understanding of materials, systems and processes.
Students will these develop skills for further education, work and life:
Assessments - In Year 10, the students will be assessed at the end of each term on written assessment that prepare the students for the GCSE exam which they will sit in Year 11. They will also be assessed on practical skills learnt and developed each term. In Term 6 of Year 10, students will get their GCSE design brief set by the exam board.
In Year 11, the students will be assessed in two component areas. Component 1 is a written examination that is 2 hours long that is based on a mixture of short answer, structured and extended writing questions to assess the student’s knowledge and understanding of technical principles, designing and making principles along with their ability to analyse and evaluate design decision and wider issues in design and technology. This is 50% of the qualification. Component 2 is a design and make task (coursework based) that is based on a contextual challenge (briefs) set by the exam board, assessing the student’s ability to, identify, investigate and outline design possibilities, design and make prototypes and analyse and evaluate design decisions and wider issues in design and technology.
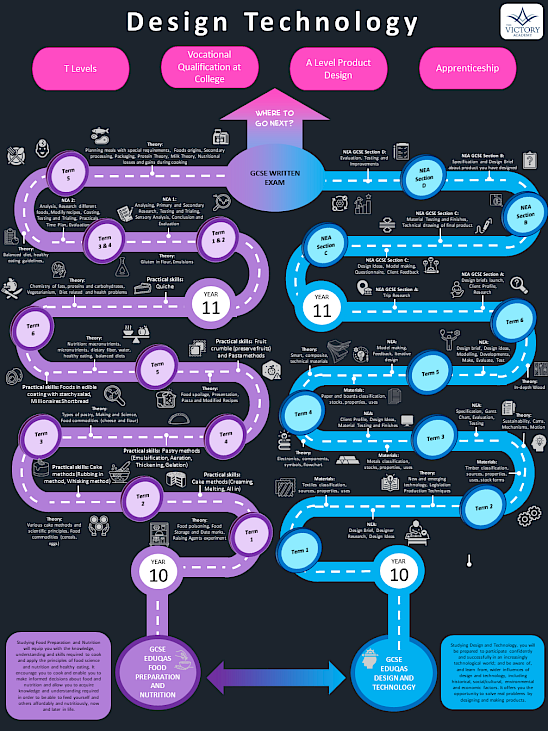
Product Design - Year 10 covers a broad range of disciplines, knowledge and skills. Student will be expose to the material areas of Textiles, Ferrous and Non-Ferrous metals, Papers and Boards, Electronics, Mechanisms, Timbers and Man Mande Boards and Polymers. This will be deepening students learning from KS3 whilst teaching students critical knowledge for the GCSE.
Food Technology - Year 10 culminates student’s experiences from KS3 as we push them further into the field of Food and Nutrition. Here, students gain a deeper understanding of Nutrition, Ingredients and their seasonal availability and safe Food practices. The course also entails some Scientific experimentations with food to understand how and why we cook food – including digestion, taste, texture and appearance and avoiding food contamination.
Product Design - For term 6 of Year 10 and the rest of year 11, students focus on their Non-Examination Assessment. This consists of following design process and developing an iterative sketchbook to develop ideas and design, plan, make and evaluate a product to solve a problem of their own development. Alongside this, students will also prepare for the exam which covers all the material areas and wider principles covered in KS3 and KS4, whilst also having the opportunity to answer exam question in Section B on their specific material area.
Food Technology - In year 11 students prepare themselves to complete their Non-Examination Assessment unit. This involves a variety of design, testing, planning, making and evaluating dishes to meet a specific target market’s requirement. This, in turn, covers much of the theory elements taught at KS3 and KS4 and apply this in a practical and realistic way. Students will also have to complete an examination where they will apply their knowledge and understanding to theoretical scenarios.
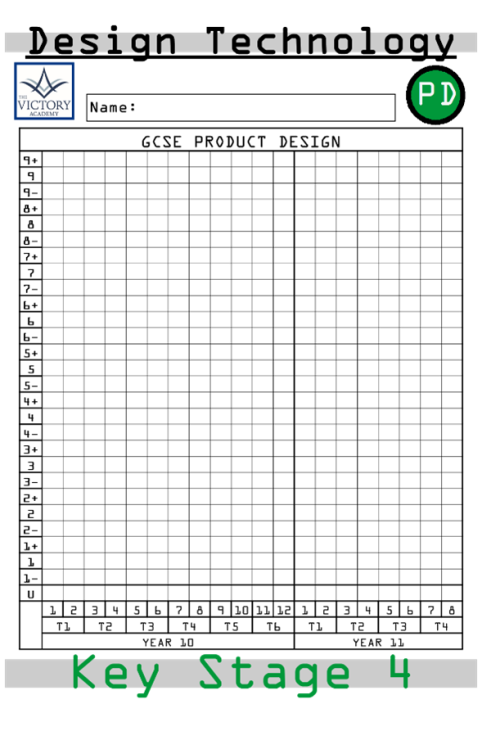
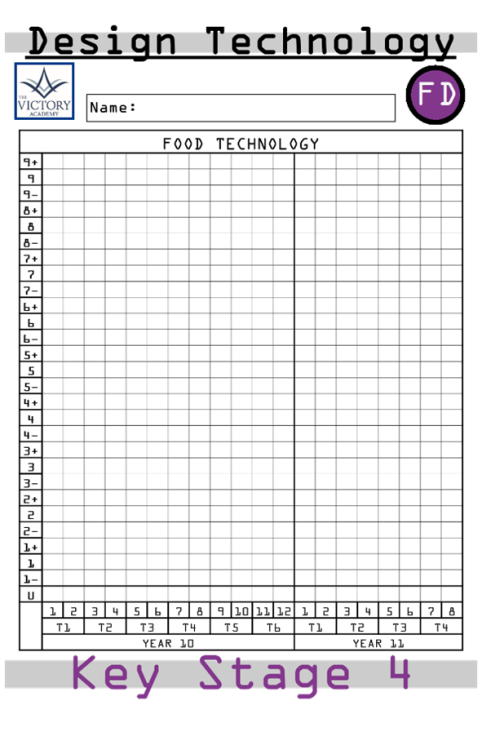
Throughout the two courses of Design and Technology, students will complete written and practical assessments at the end of every term that will be recorded of the students’ front cover. The teacher will place a highlighted line from the start of Term 1 in Year 10 to Term 4 in Year 11 which is the students target grade. Students will then input their data into the sheet so that they can view the progress that they produced throughout the two year course.
Students also have a health and safety policy to sign, similar to that as Key Stage 3. Teachers may also report training students on hand tools and machinery which will be located in the folder.
After GCSE the students have the ability of choosing AQA A-Level Product Design which offers an exciting opportunity to develop advanced skills in creativity, problem-solving, and design innovation. This course builds on prior knowledge from GCSE Design and Technology or equivalent qualifications and requires a strong foundation in technical and practical skills. Students will explore real-world design challenges, applying their knowledge of materials, processes, and emerging technologies to create functional and imaginative products. Entry requirements typically include a Grade 5 or above in GCSE Design and Technology (or a related subject) and a Grade 5 in Maths to support the technical aspects of the course. A-Level Product Design equips learners with the critical thinking, design expertise, and technical skills necessary for higher education and careers in design, engineering, and the creative industries.
Students will develop skills in:
During the course, the students will undergo written assessments with the support of handwritten flashcards and also end of term assessments and mocks without flashcards. As well as coursework and practical assessments throughout. Students will record their data on the front cover sheet which also shows their end of Year 13 target grade that has been put on by the teacher in a highlighted line.
In Year 13, the students will be assessed in 4 main assessment objectives. The students will have two written examinations and one non-exam assessment (coursework) to complete.
The Weightings for A Level Design and Technology: Product Design
| Assessment Objectives | Paper 1 | Paper 2 | NEA | Overall weighting |
| AO1 | 15 | 15 | ||
| AO2 | 25 | 25 | ||
| AO3 | 7.5 | 7.5 | 10 | 25 |
| AO4 | 22.5 | 12.5 | 35 | |
| Overall weighting of components | 30 | 20 | 50 | 100 |
The marks awarded on the papers will be scaled to meet the weighting of the components. Students’ final marks will be calculated by adding together the scaled marks for each component. Grade boundaries will be set by the exam board using this total scaled mark. The scaling and total scaled marks are shown in the table below.
| Component | Maximum raw mark | Scaling factor | Maximum scaled mark |
| Paper 1 | 120 | X1 | 120 |
| Paper 2 | 80 | X1 | 80 |
| NEA | 100 | X2 | 200 |
| Total scaled mark | 400 | ||
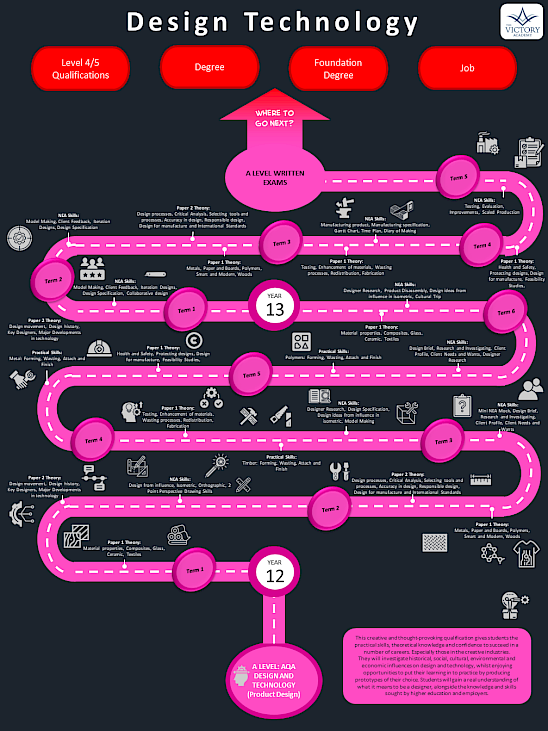
The students will build upon their knowledge of Technical Principles (Paper 1) and Designing and Making Principles (Paper 2). Students will develop the ability to draw on and apply a range of skills and knowledge from other subject areas to inform their decisions in design and the application or developments of technology. There are clear links between other subject areas such as Computer Science, Business Studies, Art and Design and History as well as Mathematics and Science.
Students will undergo a practice run of the coursework elements to ensure the students independence and marking understanding for the course as well as practical skills developing.
In Year 13 students go through their coursework to show innovation, develop intellectual curiosity about design and manufacture products and systems to do with the wider world and daily life and be able to work collaboratively to develop and refine their ideas.
The students will be marked on the ability of all of these elements as well as to skillfully produce a high-quality product and evaluate this against specification points.
At the end of the coursework, students will also be sitting two exams (Paper 1 and Paper 2) in the summer to complete this course.
Studying GCSE or A-Level Product Design opens a wealth of exciting opportunities for students, providing pathways to further education, apprenticeships, and rewarding careers. At university, students can progress to degrees in Product Design, Industrial Design, Architecture, Engineering, Graphic Design, Interior Design, or Design Technology Education. Apprenticeships are also an excellent route, offering hands-on experience in areas such as manufacturing, engineering, furniture design, and 3D prototyping.
Product Design fosters transferable skills like problem-solving, creativity, and critical thinking, which are highly valued across industries. Careers in product design, architecture, automotive design, fashion design, user experience (UX) design, set design, and even emerging fields like sustainable design and 3D printing are all possibilities. Whether students pursue further study, apprenticeships, or enter the workplace, Product Design equips them with the innovative mindset and technical expertise to succeed in today’s fast-evolving, creative, and technology-driven world.
https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/examspecs/z4nfwty
https://technologystudent.com/
https://resources.eduqas.co.uk/Pages/ResourceByArgs.aspx?subId=8&lvlId=2
https://resources.eduqas.co.uk/Pages/Food
https://www.eduqas.co.uk/media/4zjdq104/eduqas-gcse-food-preparation-nutrition-spec-from-2016.pdf
Design and Technology Revision - Seneca Learning(Spotify)
Design Better(Spotify)
Design Life(Spotify)
99% Invisible(Spotify)
GCSE Food Preparation and Nutrition Revision - Seneca Learning(Spotify)